
Forex Trading in India: What is It and How Does It Work?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is the process of exchanging one currency for another to profit from price movements. When people ask what forex trading means, it refers to participating in the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, with a daily turnover of more than $6.6 trillion. Unlike traditional stock markets, forex trading operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across key financial hubs like London, New York, and Tokyo. For Indian traders, understanding forex trading in India is especially important because the market structure, regulations, and available instruments may differ compared to other regions. Learning about forex trading and how it works can help you decide whether this global market aligns with your trading goals, whether you are seeking short-term opportunities or long-term portfolio diversification.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, means buying one currency and selling another at the same time to profit from changes in exchange rates. When beginners search for what forex trading means, they are essentially learning about the world’s largest and most liquid financial market. With a daily trading volume of over $6.6 trillion, forex trading is bigger than any other financial market globally.
All trades take place in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, where you simultaneously buy one currency and sell another. Unlike stocks, forex trading allows you to profit in both rising and falling markets, making it highly flexible. The market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial hubs like London, New York, and Tokyo.
For Indian traders, understanding forex trading in India is crucial because regulations and access may differ compared to global markets. Knowing forex trading and how it works gives you the foundation to decide whether it fits your financial goals.
In this guide, you’ll discover the fundamentals of forex trading, how the market operates, practical strategies, and the benefits of trading with TMGM, a globally recognized broker trusted by traders worldwide.
How Does Forex Trading Work
Forex trading operates much like any other financial transaction, where one asset is exchanged for another. In this case, traders buy one currency while simultaneously selling another. The price of a currency pair reflects how much of the quote currency is required to purchase one unit of the base currency. Understanding forex trading and how it works is the first step for beginners exploring global markets.
For example, if the GBP/USD pair is priced at 1.2500, it means 1 British pound is equal to 1.25 US dollars. This direct pricing structure makes it easier for Indian traders to grasp what forex trading means in practical terms.
Each currency is identified by a three-letter code, ensuring quick and accurate trade execution. Here are some of the most common codes used in forex trading in India and worldwide:
- USD – US Dollar
- EUR – Euro
- GBP – British Pound
- JPY – Japanese Yen
- AUD – Australian Dollar
These codes can help Indian traders recognize and trade currency pairs efficiently.

Figure 1: Illustrates common currency codes
Forex Trading Fundamentals
Currency Pairs Explained
All forex trading involves buying one currency while selling another, which is why currencies are always quoted in pairs. Each forex pair shows the exchange rate between two currencies, helping traders understand forex trading and how it works in practice. For beginners in India, this is a key part of learning what forex trading means.
Major Currency Pairs
Major pairs always include the US dollar (USD) paired with one of seven other major currencies, such as the euro (EUR), British pound (GBP), or Japanese yen (JPY). These forex trading pairs are the most liquid and stable, making them popular among both global and Indian traders. Major pairs account for nearly 75% of all forex trading volume worldwide, with EUR/USD being the most actively traded.
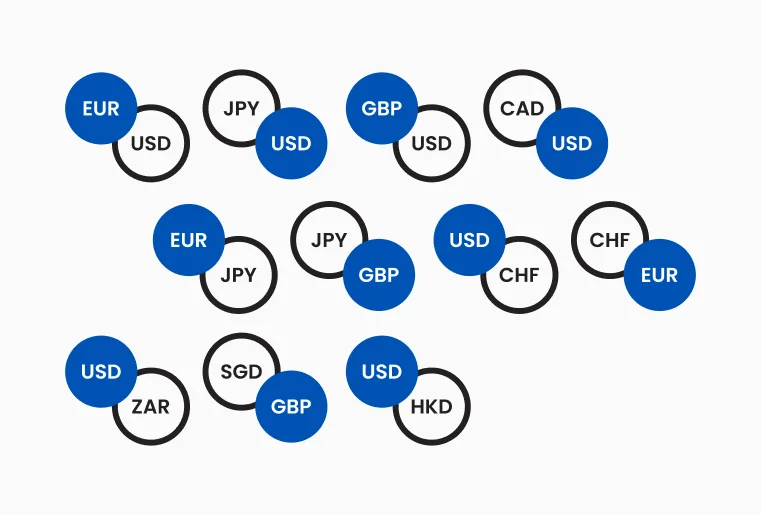
Figure 2: Illustrates major currency pairs
Minor and Exotic Pairs
Minor pairs are combinations of major currencies that do not include the US dollar (USD). Examples include EUR/GBP or GBP/JPY. Exotic pairs combine a major currency with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy, such as USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR.
Understanding Currency Pair Quotes
Every forex trading pair quote contains two prices:
- Bid price – the price at which you can sell the base currency
- Ask price – the price at which you can buy the base currency
The difference between the bid and ask is called the spread. For anyone learning forex trading and how it works, spreads represent one of the main transaction costs to consider when entering or exiting a trade.
Base and Quote Currencies

Figure 3: Illustrates base and quote currencies
In the EUR/USD pair:
- EUR is the base currency
- USD is the quote currency
- If EUR/USD is quoted at 1.2000, it means 1 euro equals 1.20 US dollars.
Understanding Pips and Lots in Forex Trading

Figure 4: Illustrates one pip
What is a Pip in Forex?
A forex pip (percentage in point) is the smallest standardized movement in price during forex trading:
- For most currency pairs: a 0.0001 change in price (fourth decimal place)
- For pairs involving the Japanese yen: a 0.01 change in price (second decimal place)
For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.2000 to 1.2001, that equals one pip. Some brokers also use pipettes (fractional pips), which represent 1/10 of a pip and are shown as the fifth decimal place.
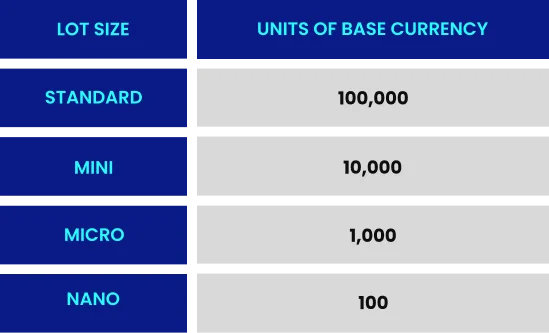
What is a Lot in Forex Trading?

Figure 5: Illustrates one lot
In forex trading, a “lot” is the standardized unit that defines the size of a trade. One standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency, while a nano lot is only 100 units of the base currency. The bigger the lot size, the greater the impact of each pip movement.
Calculating Profit and Loss
To calculate profit or loss in forex trading:
- Long position (buying): (Closing Price – Opening Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
- Short position (selling): (Opening Price – Closing Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
Example:
- Currency pair: EUR/USD
- Trade: Buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) at 1.2000
- Closing: Sell at 1.2050
- Profit: (1.2050 – 1.2000) × 100,000 = $500 profit
By learning pips, lots, and how profit/loss is calculated, Indian traders can better understand what forex trading is and make informed decisions on trade sizes and risk levels.
What is Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading?
What is Leverage in Forex?
In forex trading, leverage allows traders to control a large position with relatively small capital. Expressed as a ratio (for example, 30:1), it means you can open a position 30 times larger than your invested amount.
Leverage can work both ways:
- It magnifies potential profits from favorable market movements.
- It also magnifies potential losses when the market moves against you.
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin is the deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position in forex trading. It acts as collateral to support the leveraged exposure.
Types of Margin
- Initial Margin: The percentage of the trade value required to open a position. For instance, with 30:1 leverage, the initial margin requirement is just 3.33% of the position’s total value.
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum balance needed to keep a trade open. If your equity falls below this, you may face a margin call or automatic closure of your positions.
How to Calculate Margin in Forex Trading
Example calculation:
- Pair: EUR/USD
- Position size: 1 standard lot (100,000 EUR)
- Exchange rate: 1.2000
- Position value: $120,000
- Leverage: 30:1
- Initial margin = $120,000 ÷ 30 = $4,000
Risk Management with Leverage
Leverage can accelerate both profits and losses, so effective risk management is vital. Indian traders exploring what forex trading means should keep these practices in mind:
- Use proper position sizing (risking no more than 1–2% of your account per trade).
- Set stop-loss orders to control downside risk.
- Aim for a favorable risk-reward ratio, ideally 1:2 or better.
- Consider using lower leverage than the maximum offered.
- Stress test your trades under volatile market conditions.
Managing leverage wisely ensures controlled risk exposure and long-term sustainability in forex trading.
What is a Forex Market?
The forex trading market is decentralized and operates over the counter (OTC). Rather than a central exchange, transactions occur electronically between banks, brokers, institutions, and retail traders worldwide.
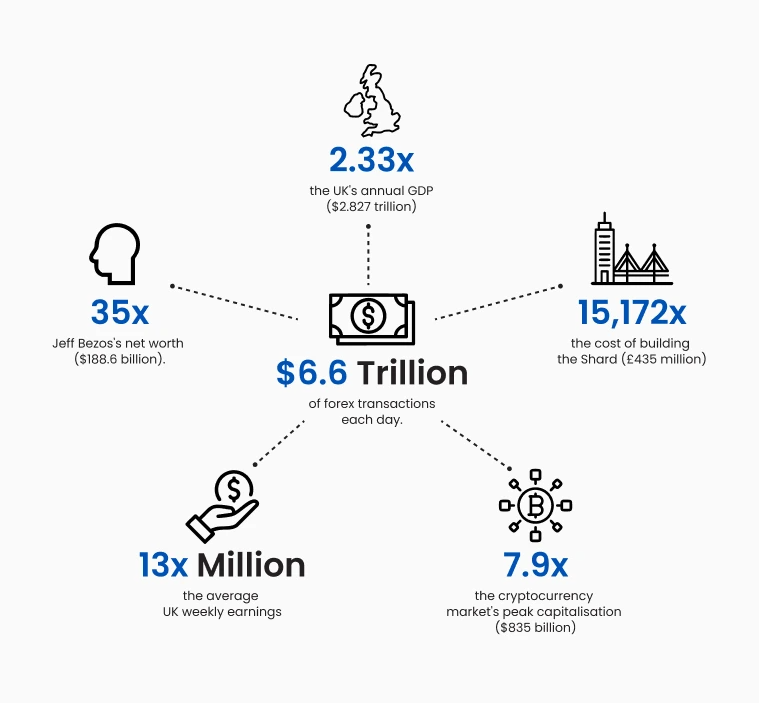
Figure 6: Illustrates the forex transactions each day
With over $6.6 trillion traded daily, it is the largest and most liquid market globally, dwarfing the daily turnover of many stock exchanges.
The Evolution of Forex Trading
The forex market has evolved dramatically over the decades:
- Pre-1970s: Fixed exchange rates under the Bretton Woods system
- 1971: Move to floating exchange rates after Bretton Woods collapsed
- 1980s–1990s: Rise of electronic trading platforms for institutions
- Early 2000s: Expansion of online retail brokers, making forex trading accessible for individuals, including traders in India
- Present day: Advanced algorithmic strategies, mobile trading platforms, and cross-asset integration
Today, forex trading represents a sophisticated global network where central banks, commercial banks, investment firms, corporations, and retail traders continuously interact.
What Moves the Forex Market?
Economic Factors
Central Bank Policies
In forex trading, central banks play a decisive role in shaping monetary policy, which directly impacts currency values. Interest rates are the most influential tool: higher interest rates usually strengthen a currency by attracting foreign investment, while lower rates can weaken it. Policies such as quantitative easing (QE) add liquidity and often weaken a currency, while quantitative tightening (QT) removes liquidity and can lead to appreciation.
Traders worldwide closely monitor statements and decisions from central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of Japan (BOJ), Bank of England (BOE), and Swiss National Bank (SNB). Their policy changes often drive sharp moves in exchange rates, influencing both short-term and long-term trading opportunities.
Economic Indicators
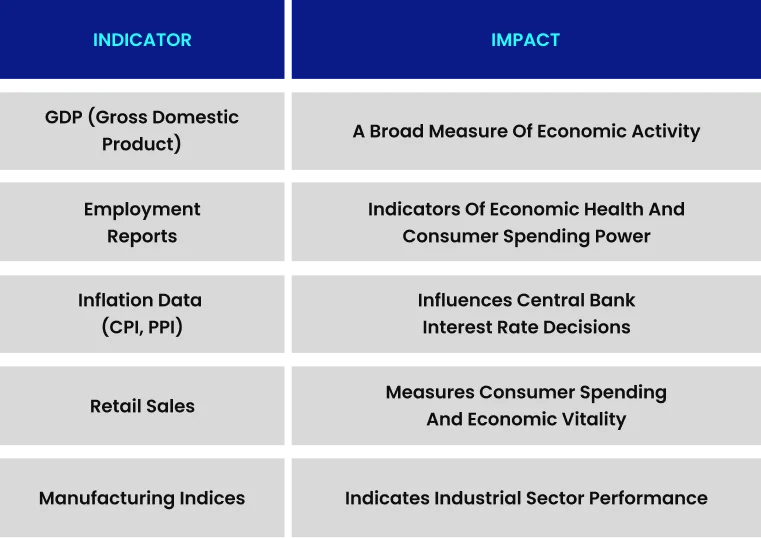
Geopolitical Events
Political and global developments also shape forex trading trends:
- Elections: Leadership changes can affect fiscal and monetary policy.
- Trade agreements or disputes: These alter economic relationships between countries.
- Regional conflicts: Create uncertainty, driving traders to safe-haven currencies like USD, JPY, or CHF.
- Regulatory changes: New rules on capital flows or financial systems can shift currency demand.
Market Psychology
Market Sentiment
While fundamentals drive long-term trends, market psychology often shapes short-term price action in forex trading.
- Risk-On vs. Risk-Off: In risk-on periods, traders seek higher-yield currencies like AUD or NZD. In risk-off phases, safer options like USD, JPY, and CHF see inflows.
- Technical Levels: Support and resistance points often become self-fulfilling triggers for breakouts or reversals.
- Positioning Reports: Data such as the Commitment of Traders (COT) report reveal where the market may be overextended, hinting at possible reversals.
For beginners learning what forex trading means, understanding sentiment is crucial. By aligning with prevailing market bias, Indian traders can better anticipate potential shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Trade Forex with TMGM

TMGM, recognized with the Best Multi-Asset Broker APAC award at the 2024 Brokersview ceremony, continues to set industry standards in forex trading and multi-asset brokerage. For traders in India, TMGM offers a reliable, technology-driven platform designed to support every step of your trading journey.
Why Choose TMGM for Forex Trading
As a globally trusted broker, TMGM delivers competitive conditions and advanced tools that align perfectly with the needs of those exploring forex trading in India.
- Ultra-tight spreads: Starting from 0.0 pips on major currency pairs with competitive commissions.
- High leverage options: Access leverage of up to 1:1000, giving Indian traders flexibility in position sizing.
- Deep liquidity: Orders are executed efficiently through tier-1 providers, with average execution speeds under 30 milliseconds to minimize slippage.
- Versatile platforms: Trade on MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5) across PC, Mac, tablets, and mobile devices.
- Comprehensive support: Multilingual assistance, dedicated account managers, and smooth withdrawal processing.
TMGM also invests in trader education through its Trading Academy, daily market analysis, real-time economic calendar, and interactive webinars. For Indian beginners searching for what forex trading means, these resources make it easier to understand the fundamentals while building confidence step by step.
Free Forex Trading Courses and Resources
Becoming a successful trader takes practice, discipline, and knowledge. TMGM provides free forex trading courses, live webinars, and market insights tailored to traders of all levels. New clients can start with a free demo account that comes with US$100,000 in virtual funds, allowing them to practice strategies risk-free before entering live markets.
Trade Smarter Today




FAQs on Forex Trading with TMGM
Is TMGM a reliable broker for forex trading in India?
Can I open a demo account with TMGM to learn what is forex trading meaning?
What trading resources does TMGM provide for Indian forex traders?
Does TMGM offer high leverage and tight spreads for forex trading?

Account
Account
Instantly



